Peas are delightful to grow and can thrive in various climates. Let’s explore the recommended growing zones, examples of US states within those zones, and whether you can grow them indoors:
Growing Zones for Peas:
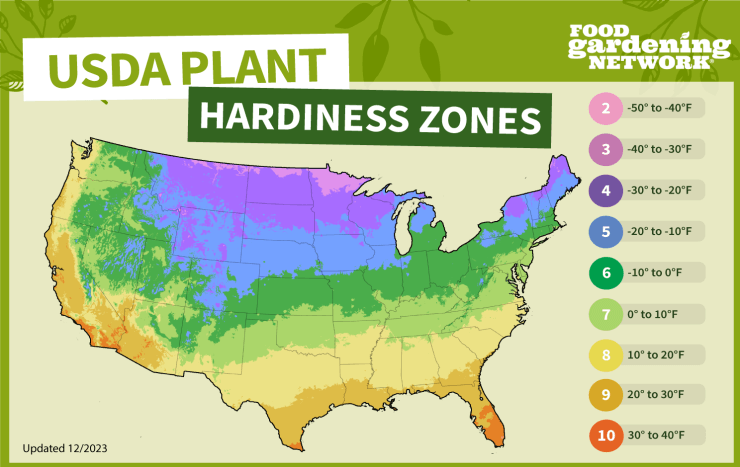
Peas can be grown in a wide range of USDA hardiness zones. The recommended zones for peas span from Zone 3 to Zone 11. These zones cover most of the United States, allowing gardeners across the country to enjoy fresh peas.
Examples of US States in Growing Zones:
Here are some states associated with specific growing zones:
- Zone 3: Includes parts of Minnesota, where hardy peas can withstand cold winters.
- Zone 7: Encompasses regions like Washington, Oregon, and Idaho, which are excellent for pea cultivation.
- Zone 9 and 10: In these warmer zones, such as Florida, Texas, and California, consider planting peas in the fall, winter, or early spring.
- Zone 11: Includes tropical areas like Hawaii, where peas can thrive year-round.
Growing Peas Indoors:
Yes, you can grow peas indoors! Here’s how:
- Light: Indoor pea plants need 8 to 10 hours of bright light. Place them in the sunniest spot in your home or use grow lights.
- Varieties: Opt for varieties like snap peas, snow peas, or dwarf peas, as they adapt well to containers and indoor conditions.
- Soil: Use a purchased seed starter mix or create your own by combining equal parts potting soil and compost.
- Sowing: Sow seeds in flats or small containers, keeping them about 2 inches apart. Keep the soil consistently moist.
- Support: As the shoots grow, provide support using a mini trellis or wire system to keep the vines upright.
- Harvest: Pea pods will form quickly, usually within 60 days. Harvest when the pods are firm and deeply green
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map here. Or, for a quick glance at your general plant hardiness zone, use our map.
Remember, growing peas indoors allows you to enjoy fresh pods even if you have limited outdoor space. Happy gardening!


 Previous
Previous

