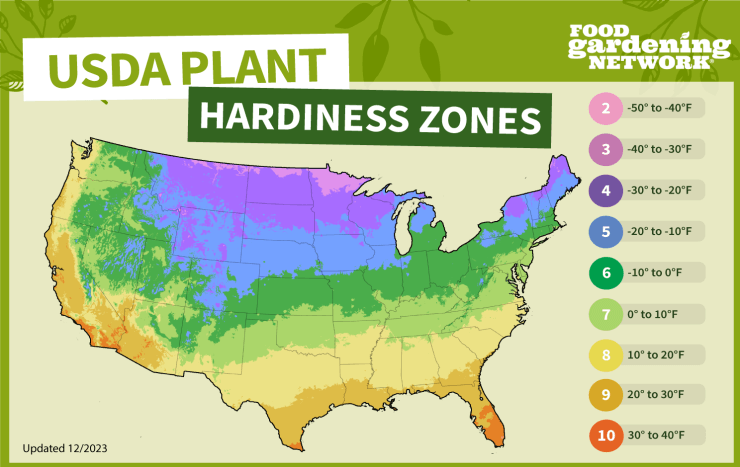
Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus) thrive in USDA Hardiness Zones 4 through 12. These zones cover a wide range of climates across the United States, making cucumbers a versatile crop for many gardeners. Here’s a breakdown of the zones and some example states:
Recommended Growing Zones for Cucumbers
- Zones 4-6: These zones cover the cooler regions of the United States. While cucumbers can grow in these zones, they may require more careful management of planting times to avoid frost. Examples include:
- Zone 4: Northern parts of Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana.
- Zone 5: Southern parts of Minnesota, parts of Iowa, Nebraska, and Massachusetts.
- Zone 6: Areas of Missouri, Kansas, Kentucky, and parts of the Northeast such as Pennsylvania and New York.
- Zones 7-9: These zones are ideal for cucumber growth due to their longer growing seasons and milder winters. Examples include:
- Zone 7: Parts of Virginia, Tennessee, and Oklahoma.
- Zone 8: Much of the Southeast, including Georgia, South Carolina, and parts of Texas.
- Zone 9: Coastal areas and parts of the Southwest, including southern California, southern Texas, and Florida.
- Zones 10-12: These zones, which are very warm year-round, are also suitable for cucumber growing, although intense summer heat may require some shade or additional watering. Examples include:
- Zone 10: Southern Florida, parts of southern Texas, and southern California.
- Zone 11: Tropical areas such as Hawaii and parts of southern Florida.
- Zone 12: Very limited in the continental US but includes tropical islands.
Indoor Growing
Yes, cucumbers can be grown indoors, which is especially useful for those in regions with shorter growing seasons or limited outdoor space. Here are some tips for growing cucumbers indoors:
- Container Selection: Use large containers that are at least 12 inches deep and wide to allow enough space for root growth.
- Lighting: Cucumbers need plenty of light, at least 8 hours of direct sunlight per day. If natural light is insufficient, use grow lights to supplement.
- Temperature: Maintain a consistent temperature between 70-85°F (21-29°C) for optimal growth.
- Support: Provide a trellis or support system for vining cucumber varieties to climb.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Good drainage is crucial.
- Pollination: If growing indoors without insects, you may need to hand-pollinate flowers to ensure fruit set.
By following these guidelines, cucumbers can be successfully grown in a variety of climates and even indoors, allowing gardeners to enjoy fresh cucumbers nearly year-round.
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map here. Or, for a quick glance at your general plant hardiness zone, use our map.


 Previous
Previous

