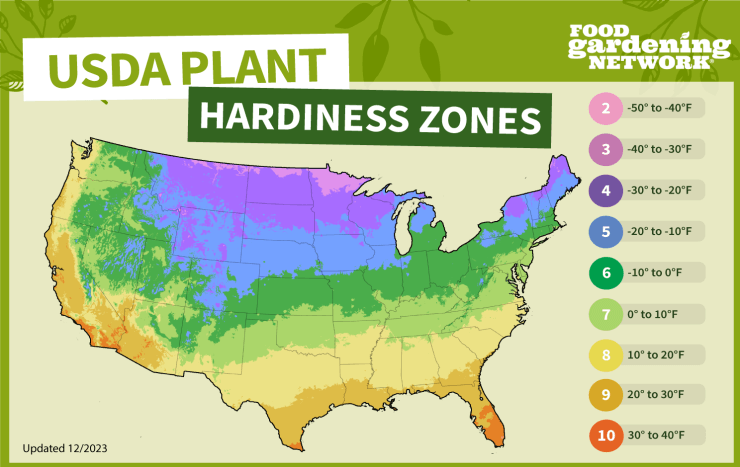
Kale is a cold-hardy leafy green that can tolerate a range of temperatures. It is generally recommended to grow kale in USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 7 to 10, although it can also thrive in zones 2 to 6 with proper care. Here are examples of U.S. states that fall within these zones:
Zone 2: Some states in this zone are:
- Northern parts of Alaska
Zone 3: Some states in this zone are:
- North Dakota
- Montana
- Northern parts of Minnesota
Zone 4: Some states in this zone are:
- Minnesota (excluding the northernmost parts)
- Wisconsin
- Michigan
- Maine
- Vermont
- New Hampshire
- New York (excluding the northernmost parts)
- Massachusetts
- Connecticut
- Rhode Island
Zone 5: Some states in this zone are:
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Ohio
- Pennsylvania
- New York (including the northernmost parts)
- Most of New Jersey
Zone 6: Some states in this zone are:
- Southern parts of Illinois
- Southern parts of Indiana
- Southern parts of Ohio
- Southern parts of Pennsylvania
- Southern parts of New York
- Southern parts of New Jersey
Zone 7: Some states in this zone are:
- Most of Maryland
- Most of Virginia
- Most of North Carolina
- Most of South Carolina
- Most of Tennessee
- Most of Arkansas
- Parts of Oklahoma
- Parts of Texas
- Most of Georgia
- Most of Alabama
- Most of Mississippi
- Most of Louisiana
Zone 8: Some states in this zone are:
- Most of Texas
- Southern parts of Louisiana
- Southern parts of Mississippi
- Southern parts of Alabama
- Southern parts of Georgia
- Southern parts of South Carolina
- Southern parts of North Carolina
- Southern parts of Virginia
Zone 9: Some states in this zone are:
- Southern parts of California
- Southern parts of Arizona
- Southern parts of Texas
- Southern parts of Louisiana
- Southern parts of Florida
- Parts of Nevada
- Parts of New Mexico
Zone 10: Some states in this zone are:
- Most of Southern Florida
- Coastal areas of Southern California
- Southern parts of Texas (closer to the coast)
- Southern parts of Arizona (lower elevations)
- Parts of Hawaii
As you can see, kale can be grown in a wide range of climates across the U.S. It is a versatile vegetable that can withstand frost and even thrive in colder temperatures.
Regarding growing kale indoors, it is definitely possible with the right conditions. Similar to other vegetables, indoor kale cultivation requires attention to certain factors:
- Light: Kale requires a good amount of sunlight to grow properly. Place the kale plants near a south-facing window or use artificial grow lights to ensure they receive at least six hours of direct or indirect sunlight daily.
- Temperature: Kale prefers cool temperatures, ideally between 60 to 70 degrees F. It can tolerate slightly warmer temperatures but may bolt (go to seed) in prolonged heat.
- Space: Make sure the indoor setup provides enough space for the kale plants to grow and spread out.
- Soil: Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil with a slightly acidic pH for indoor kale plants.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Adequate drainage is essential to prevent root rot.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer or one that is higher in nitrogen to promote leafy growth.
- Pest control: Monitor for common indoor pests and take appropriate measures to control them if necessary.
With proper care and attention to its requirements, kale can be successfully grown indoors, allowing you to enjoy this nutritious green even if you have limited outdoor gardening space.
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and find out what zone your zip code is located in here. Or you can use our map to get a general idea of what your plant hardiness zone is.


 Previous
Previous

