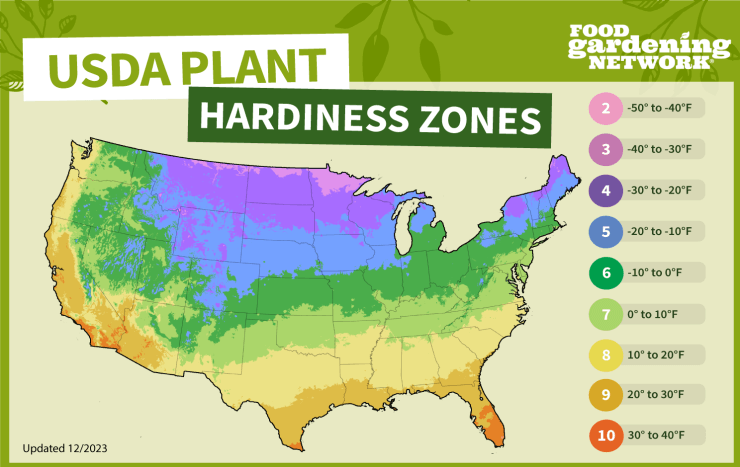
Green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) are versatile and can be grown in a wide range of climates. They thrive in USDA Hardiness Zones 3 through 10. Here’s a breakdown of the zones and some example states:
Recommended Growing Zones for Green Beans
- Zones 3-5: These zones cover cooler regions of the United States. Green beans can be grown here, but the growing season is shorter. Examples include:
- Zone 3: Northern parts of Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana.
- Zone 4: Areas of Wisconsin, northern New York, and parts of New England.
- Zone 5: Much of the Midwest, including Iowa, Nebraska, and parts of Ohio.
- Zones 6-8: These zones are ideal for green beans due to their longer growing seasons and milder temperatures. Examples include:
- Zone 6: Parts of Missouri, Kentucky, Pennsylvania, and the Mid-Atlantic region.
- Zone 7: Parts of Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Oklahoma.
- Zone 8: The Southeast, including Georgia, South Carolina, and parts of Texas.
- Zones 9-10: These warmer zones allow for multiple harvests per year but may require some shading or additional watering during the hottest months. Examples include:
- Zone 9: Coastal areas of California, southern Texas, and Florida.
- Zone 10: Southern Florida and parts of southern Texas and southern California.
Indoor Growing
Yes, green beans can be grown indoors, which is beneficial for those with limited outdoor space or in regions with unsuitable climates for outdoor growing. Here are some tips for growing green beans indoors:
- Container Selection: Use containers that are at least 8-10 inches deep. Bush varieties are more suitable for containers than pole varieties due to their compact growth habit.
- Lighting: Green beans need plenty of light, ideally 8-10 hours of direct sunlight per day. Use grow lights if natural light is insufficient.
- Temperature: Maintain a consistent temperature between 60-75°F (15-24°C) for optimal growth.
- Support: If growing pole beans, provide a trellis or stakes for the vines to climb. Bush beans generally do not require support.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but ensure good drainage to avoid waterlogging. Water regularly and monitor the moisture level.
- Pollination: Green beans are self-pollinating, so you don’t need to worry about hand pollination if growing indoors.
By following these guidelines, green beans can be successfully grown both outdoors in a variety of climates and indoors, providing a fresh supply of beans nearly year-round.
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map here. Or, for a quick glance at your general plant hardiness zone, use our map.


 Previous
Previous

