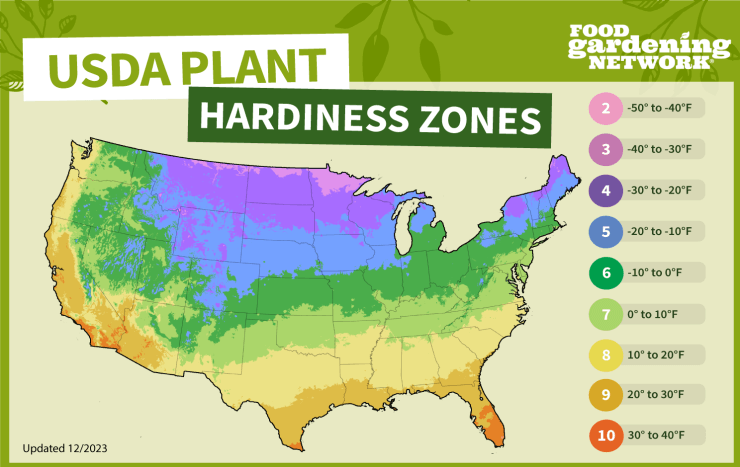
Blueberries can be grown in a wide range of climates, specifically in USDA hardiness zones 3 through 10. The recommended growing zones for blueberries vary depending on the type:
-
- Lowbush blueberries are hardy in zones 3 to 6.
- Half-high blueberries in zones 3 to 5.
- Highbush blueberries in zones 4 to 7.
For example, states like Oregon, Washington, Georgia, Michigan, California, New Jersey, North Carolina, Florida, Texas, and Minnesota are known for blueberry production, indicating they fall within the suitable growing zones.
As for growing blueberries indoors, it is indeed possible! With the right conditions, such as a sunny spot and proper soil acidity, you can enjoy blueberries year-round as a houseplant. It’s recommended to choose dwarf or lowbush varieties for indoor cultivation due to their smaller size and to ensure the soil pH is between 4 and 5.5, which is ideal for blueberries. Regular watering, ensuring full sun exposure, and possibly cross-pollinating with another plant can lead to a successful indoor blueberry garden.
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map here. Or, for a quick glance at your general plant hardiness zone, use our map.


 Previous
Previous

