Pumpkins are warm-season plants that thrive in specific growing zones. The recommended growing zones for pumpkins in the U.S. are typically zones 3 to 9. Here are some examples of states within these recommended growing zones:
Zone 3: Includes states with colder climates such as:
- Parts of Montana
- Parts of North Dakota
- Parts of Minnesota
Zone 4: Some states in this zone are:
- Wisconsin
- Michigan
- Maine
Zone 5: Some states in this zone are:
- Illinois
- Ohio
- Pennsylvania
Zone 6: Some states in this zone are:
- Virginia
- Tennessee
- Missouri
Zone 7: Some states in this zone are:
- North Carolina
- Georgia
- Arkansas
Zone 8: Some states in this zone are:
- Texas
- Louisiana
- Florida
Zone 9: Includes warm regions such as:
- Southern California
- Arizona
- Parts of Texas
- Parts of Florida
Growing pumpkins indoors is possible but not recommended for most varieties. Pumpkins are typically large, vining plants that require a lot of space, sunlight, and airflow. Growing them indoors can be challenging due to their size and the need for pollination.
However, some smaller or bush-type pumpkin varieties might be more suitable for container gardening indoors or in a greenhouse setting. These varieties are specifically bred to take up less space and can be more manageable for indoor cultivation.
If you have limited outdoor space, you might consider growing compact pumpkin varieties or other types of small gourds that are better suited for container gardening.
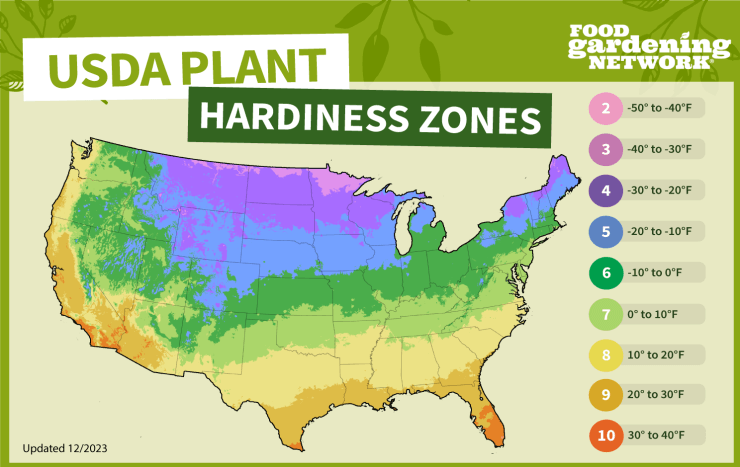
Check out the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and find out what zone your zip code is located in here. Or you can use our map to get a general idea of what your plant hardiness zone is.


 Previous
Previous

