
Lots of nutritious potatoes.
Potatoes

Lots of nutritious potatoes.
You’ve probably heard more than once that potatoes are fattening, right? Guess what? They’re not. They are one of the biggest nutritional bargains you can find. A potato about the size of a computer mouse weighs about 5 1/2 ounces. It has just 100 calories, no fat, 21% of your daily recommendation for potassium, and a whopping 45% of your daily recommendation for vitamin C (remember when we talked about preventing scurvy?).
Potatoes in and of themselves are not fattening; it’s what is put on them. Butter, bacon bits, cheese, sour cream… the list goes on and on. Want to eat healthy? Just don’t drown your baked potato in butter and sour cream, and you’ll be fine.
Here are the nutrients in a medium-sized, about 2-3 inches in diameter (170 grams), potato:
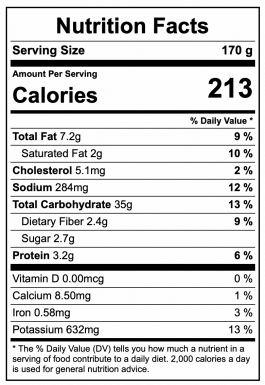
Here are some of the other great things in potatoes:
- Fiber helps with digestion and makes us feel full. Having enough fiber in your diet is tied to heart health.
- Folate, or folic acid. Helps our tissues grow and our cells work. Folic acid is especially important for pregnant women.
- This electrolyte helps build muscle and keeps your heart healthy.
- Essential for healthy red blood cells and muscles.
- B vitamin that helps our body convert carbohydrates into energy, and improves our circulation.
- B vitamin that helps our body convert carbohydrates into energy, and helps maintain a healthy nervous system.
Sweet Potatoes

Sweet potatoes are good for you, too!.
Sweet potatoes were ranked second to the Irish potato as an important vegetable until World War II. The sweet potato is packed with calcium, iron, and other minerals and vitamins, especially vitamins A and C.
Here is the nutritional breakdown of a half cup (100 grams) of cooked sweet potato:
Calories: 90
Protein: 2 grams
Carbs: 21 grams
Sugar: 6 grams
Fiber: 3 grams
Fat: 0 grams
Here are some of the other great things in sweet potatoes:
- Beta-carotene. Orange sweet potatoes are rich in vitamin A in the form of beta-carotene, which contributes to eye health.
- These are naturally occurring plant chemicals that give vegetables their color—in this case, the purple of a purple sweet potato. Anthocyanins have antioxidant properties that fight free radicals to repair cell damage.
- Manganese helps produce collagen and promotes skin and bone health.
- While the purple sweet potatoes can boast anthocyanins, the basic orange sweet potato is loaded with vitamins A and C, which have strong antioxidant properties of their own.
And the leaves of the sweet potato plant are rich in vitamin B, beta-carotene, iron, calcium, zinc, and protein. Take that, spinach!
Did you know all these nutrition facts about potatoes and sweet potatoes? Please tell us what you think.



